This is a hot topic at the moment, should you make the switch to electric or should you stick with your ICE (Internal Combustion Engine) for the time being? In this article, we will be focussing on how each works, the cost of financing, running and insuring each example. We will cover each class of vehicle from supermini through to SUVs.
What are the main differences between EVs and ICEs?
Internal Combustion Engines (ICE)
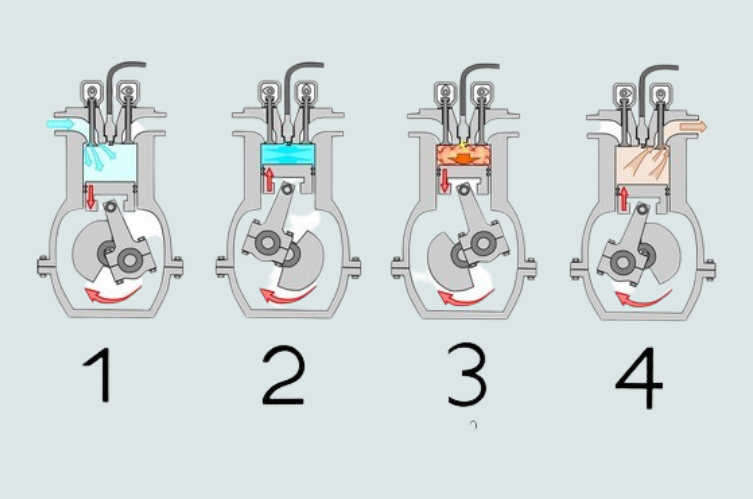
ICEs have been around for over 160 years and have been refined over the years to be more efficient and cleaner for the environment. An internal combustion engine consists of the following components: Combustion chamber, intake and exhaust valves, piston, connecting rod, crankshaft and, if applicable, a spark plug. Four steps must take place for the car do drive:
- Intake: The piston moves downwards in the combustion chamber and draws an air–petrol mixture (in the case of diesel, only air) through the intake valve into the combustion chamber.
- Compression: The piston moves upwards and thus compresses the mixture or air that has flowed in. The inlet and outlet valves are closed so that nothing can escape.
- Power: If the pressure is high enough, the spark plug produces a spark, and the mixture explodes. In the case of diesel vehicles, the fuel is injected into the combustion chamber, where it self-ignites because of the high pressure and temperature. The explosion pushes the piston down.
- Emission: The piston moves up again, the exhaust valve is open, and the exhaust gases escape.
Electric Vehicles (EV)
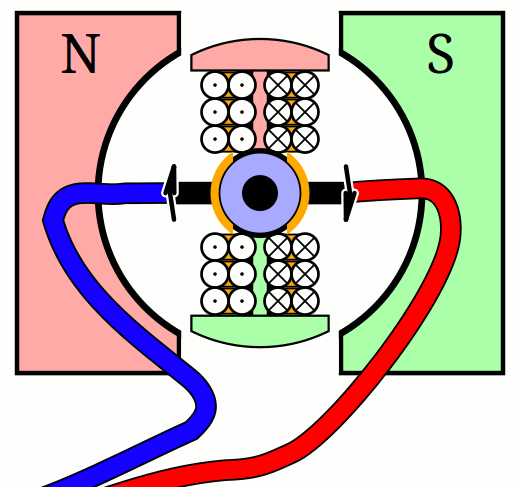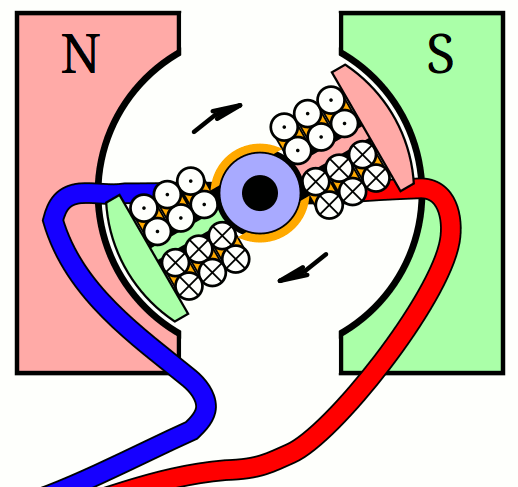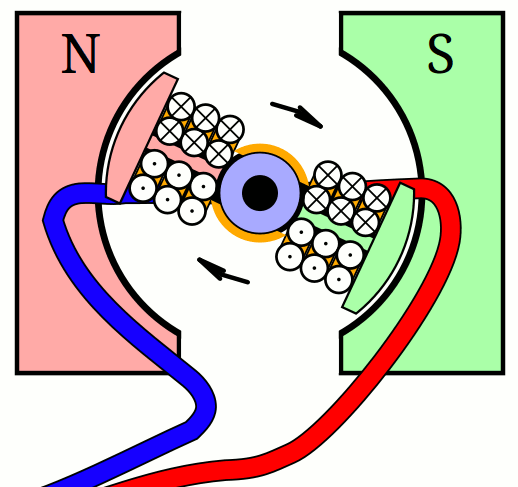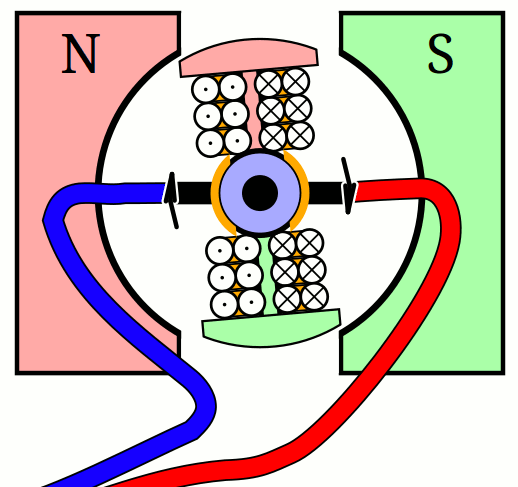
An electric motor essentially consists of two electromagnets. The housing generates a constant magnetic field through a direct current and inside is a rotating coil. As soon as the current flows through it, it also becomes magnetic. The opposite poles repel each other forcing it to rotate. In order to keep it spinning, the rotor inside must change its polarity at regular intervals.
Electric Models vs Combustion Counterparts
SuperMini: Peugeot 208 vs Peugeot e-208 (2021)
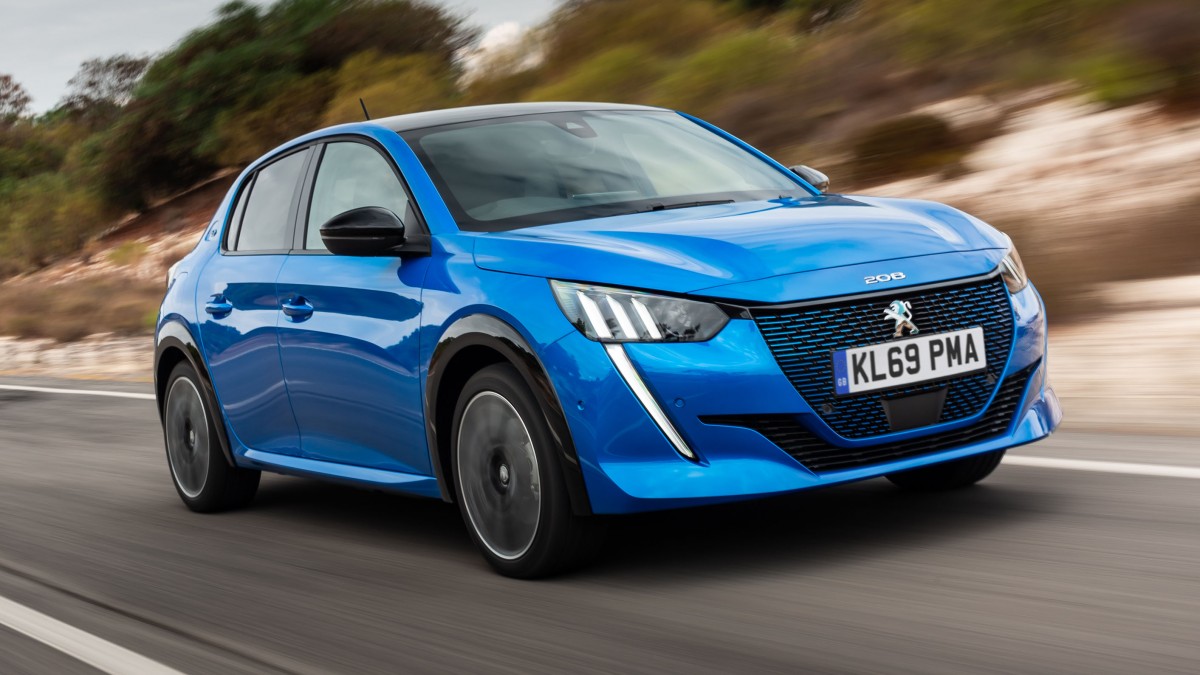


Left: Peugeot 208 | Right: Peugeot e-208
Vehicle Price: £20,795 | £29,995
Finance per Month: £406.77 | £478.92
Road Tax: £165 | £0
Ave Fuel Cost: £1.93 (Diesel per litre UK) | £1.85 (Petrol per litre UK) | 28p per kWh (£15 for 60kWh battery)
Hatchback: VW Golf vs VW e-Golf (2020)
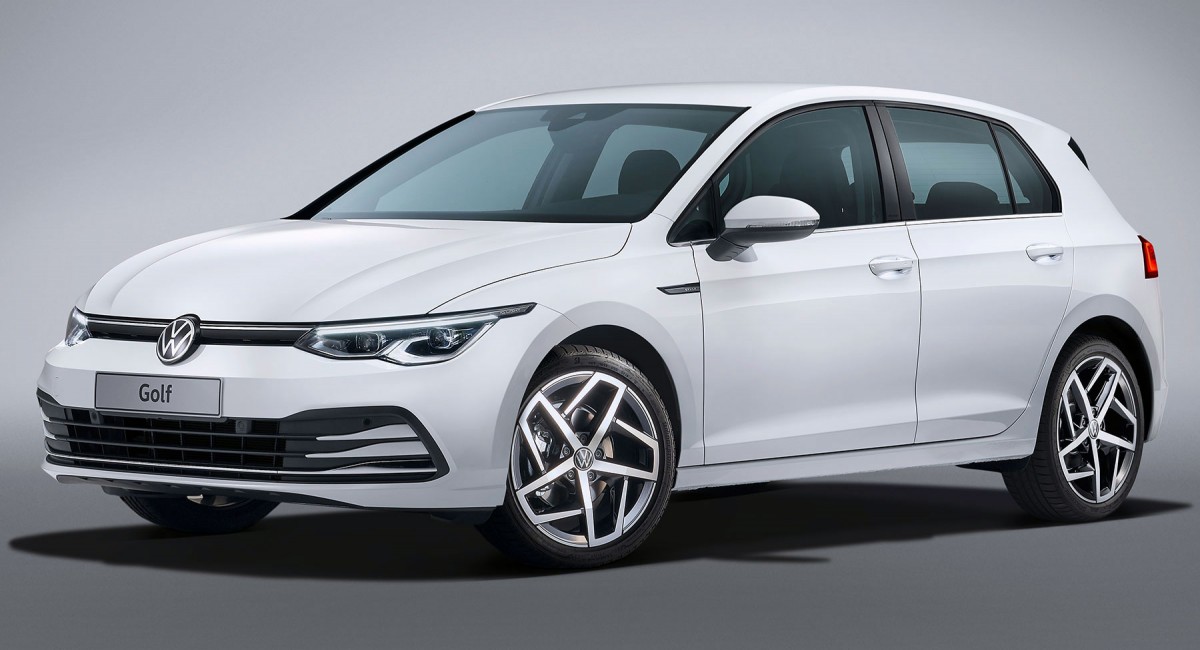
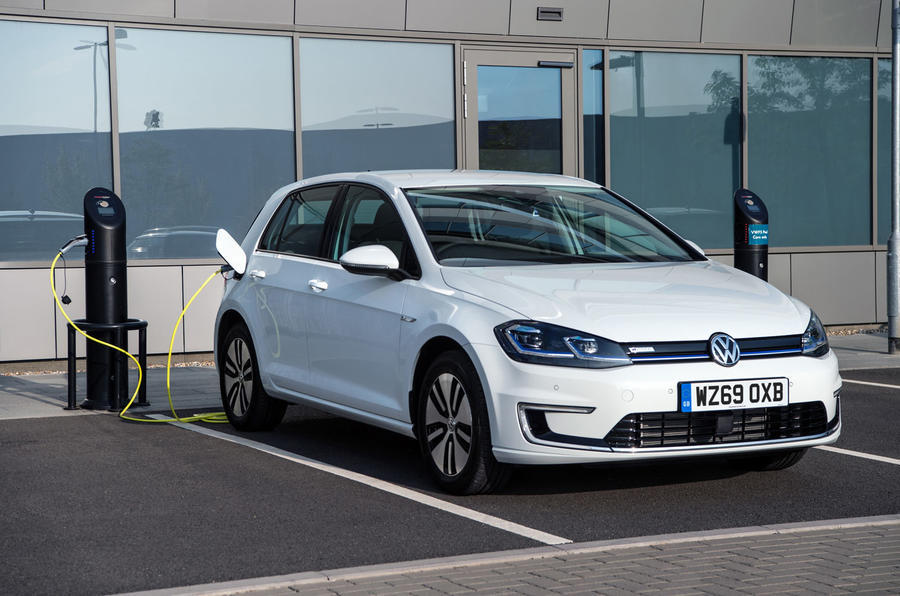


Left: VW Golf | Right: VW e-Golf
Vehicle Price: £18,995 | £22,995
Finance per Month: £277.60 | £344.96
Road Tax: £165 | £0
Ave Fuel Cost: £1.93 (Diesel per litre UK) | £1.85 (Petrol per litre UK) | 28p per kWh (£15 for 60kWh battery)
Saloon: BMW 4 Series vs BMW i4 (2021)
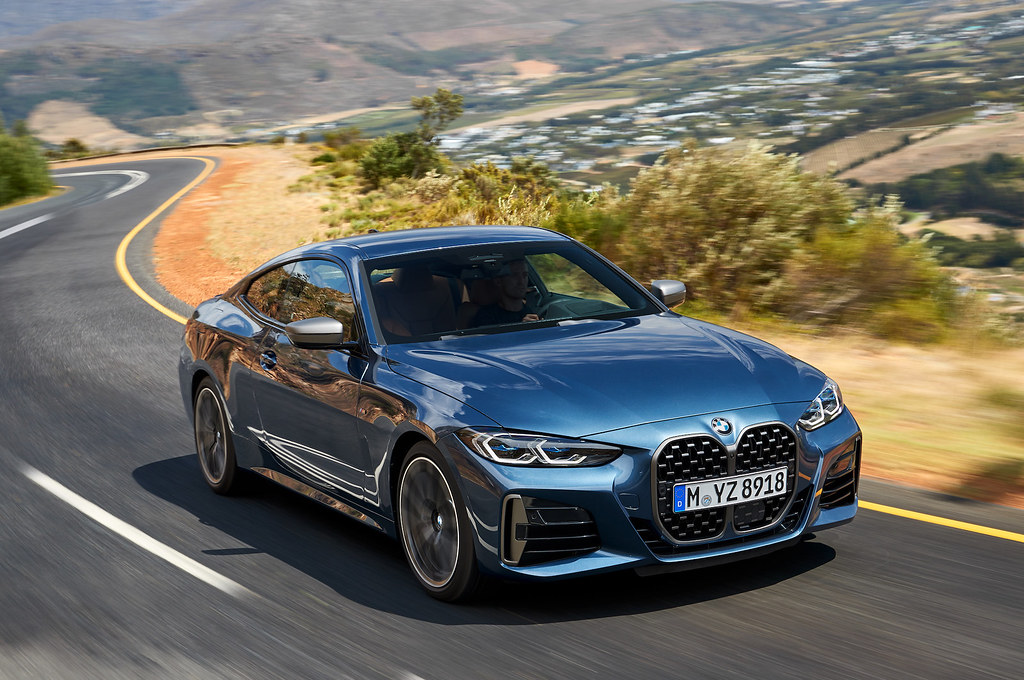
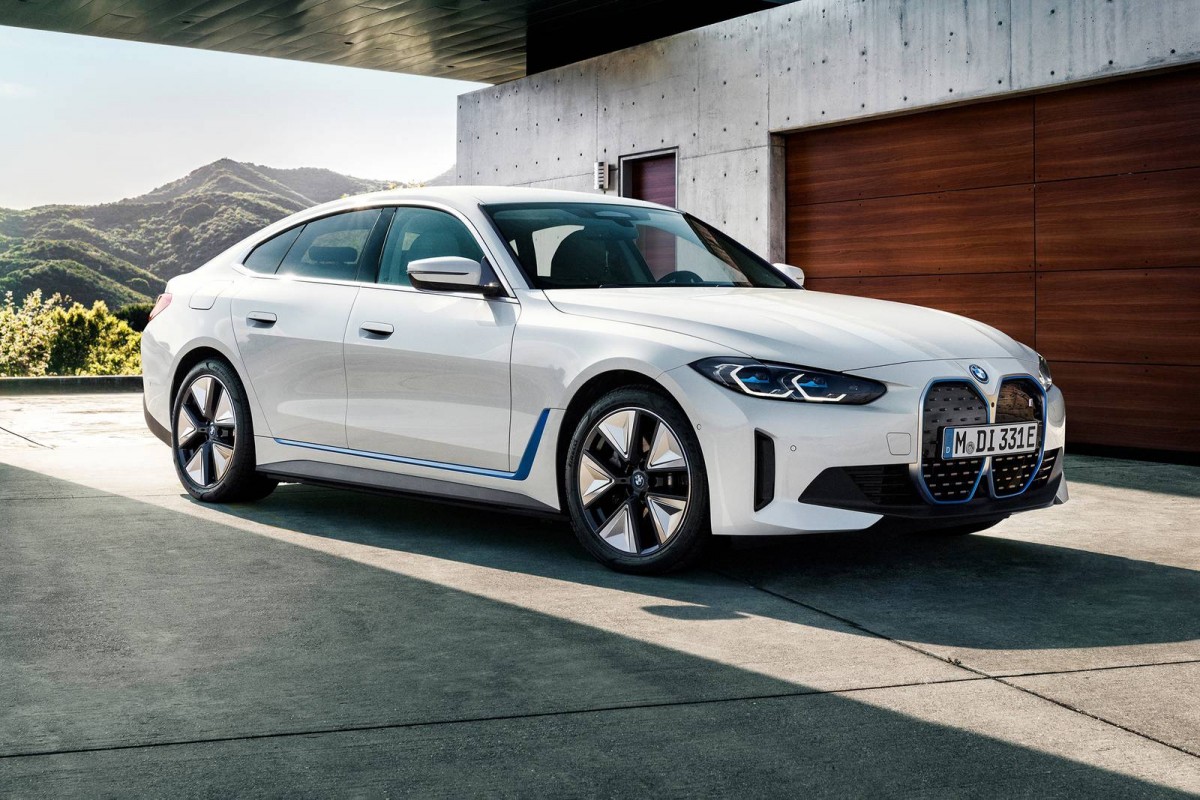


Left: BMW 4 Series | Right: BMW i4
Vehicle Price: £46,300 | £65,795
Finance per Month: £724.80 | £873
Road Tax: £520 (first 5 years) | £0
Ave Fuel Cost: £1.93 (Diesel per litre UK) | £1.85 (Petrol per litre UK) | 28p per kWh (£15 for 60kWh battery)
SUV: BMW X5 vs BMW iX (2021)
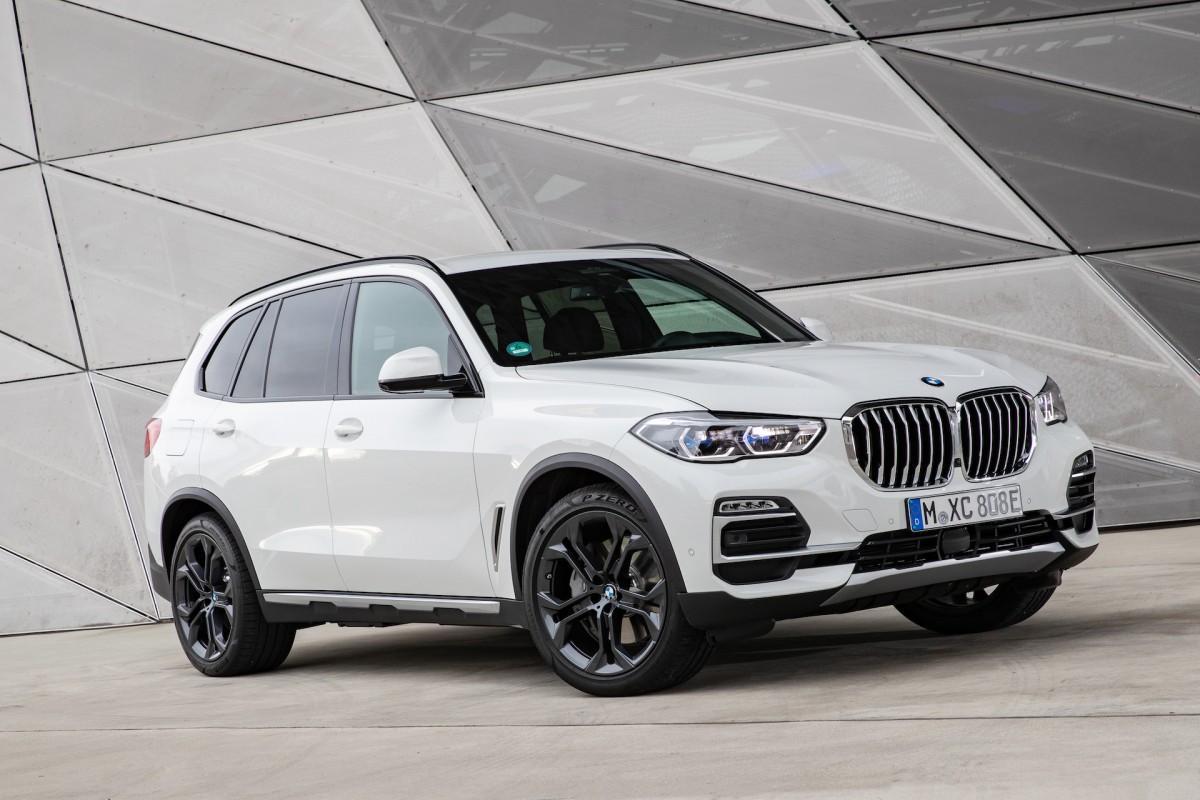
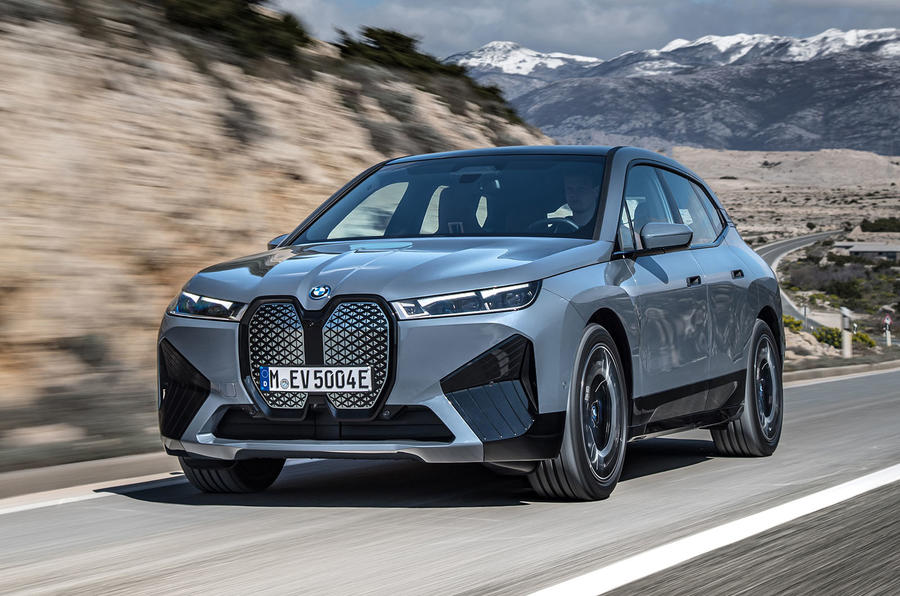


Left: BMW X5 | Right: BMW iX
Vehicle Price: £59,999 | £72,998
Finance per Month: £724.80 | £1,207
Road Tax: £520 (first 5 years) | £0
Ave Fuel Cost: £1.93 (Diesel per litre UK) | £1.85 (Petrol per litre UK) | 28p per kWh (£15 for 60kWh battery)
Sports Car: Audi RS3 vs Audi RS E-Tron (2021)
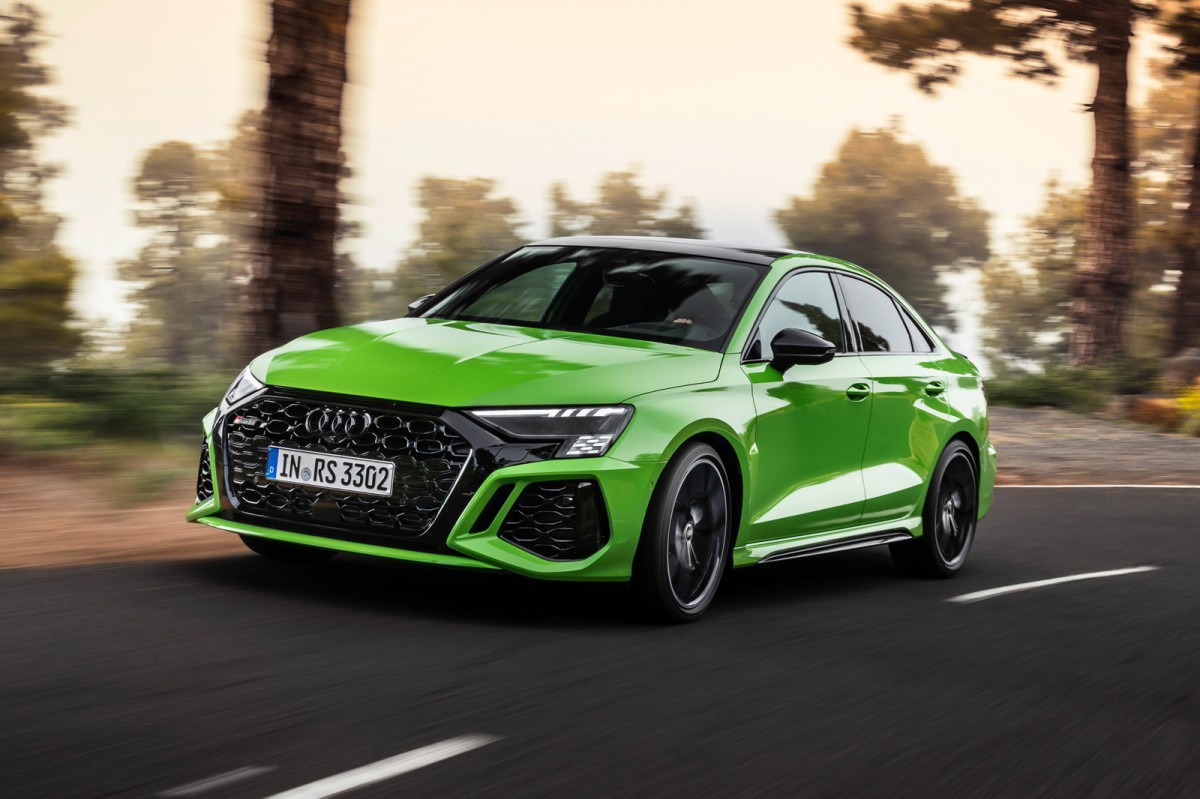

Left: Audi RS3 | Right: Audi RS e-tron
Vehicle Price: £64,995 | £119,000
Finance per Month: £958.18 | £1,907.62
Road Tax: £520 (first 5 years) | £0
Ave Fuel Cost: £1.93 (Diesel per litre UK) | £1.85 (Petrol per litre UK) | 28p per kWh (£15 for 60kWh battery)
NOTE:
All finance prices per month are calculated for PCP at a rate of 6.9% APR with a deposit of £1,000
CarMoney can help you with electric car finance.
